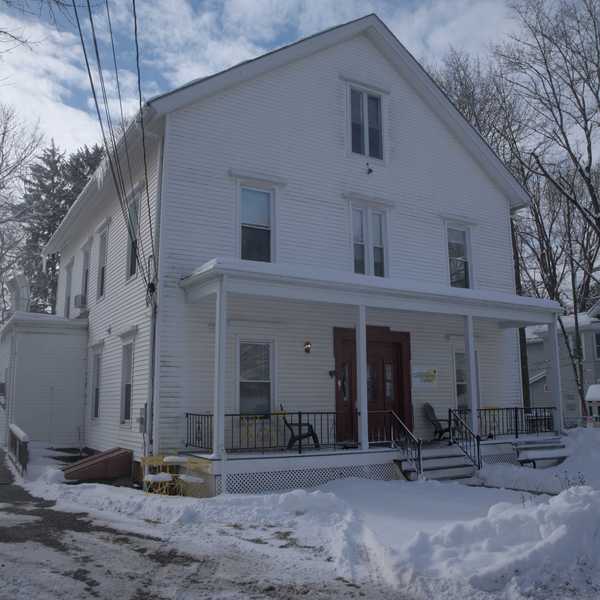
Local power: Norfolk’s link to Jimmy Carter’s White House solar panels
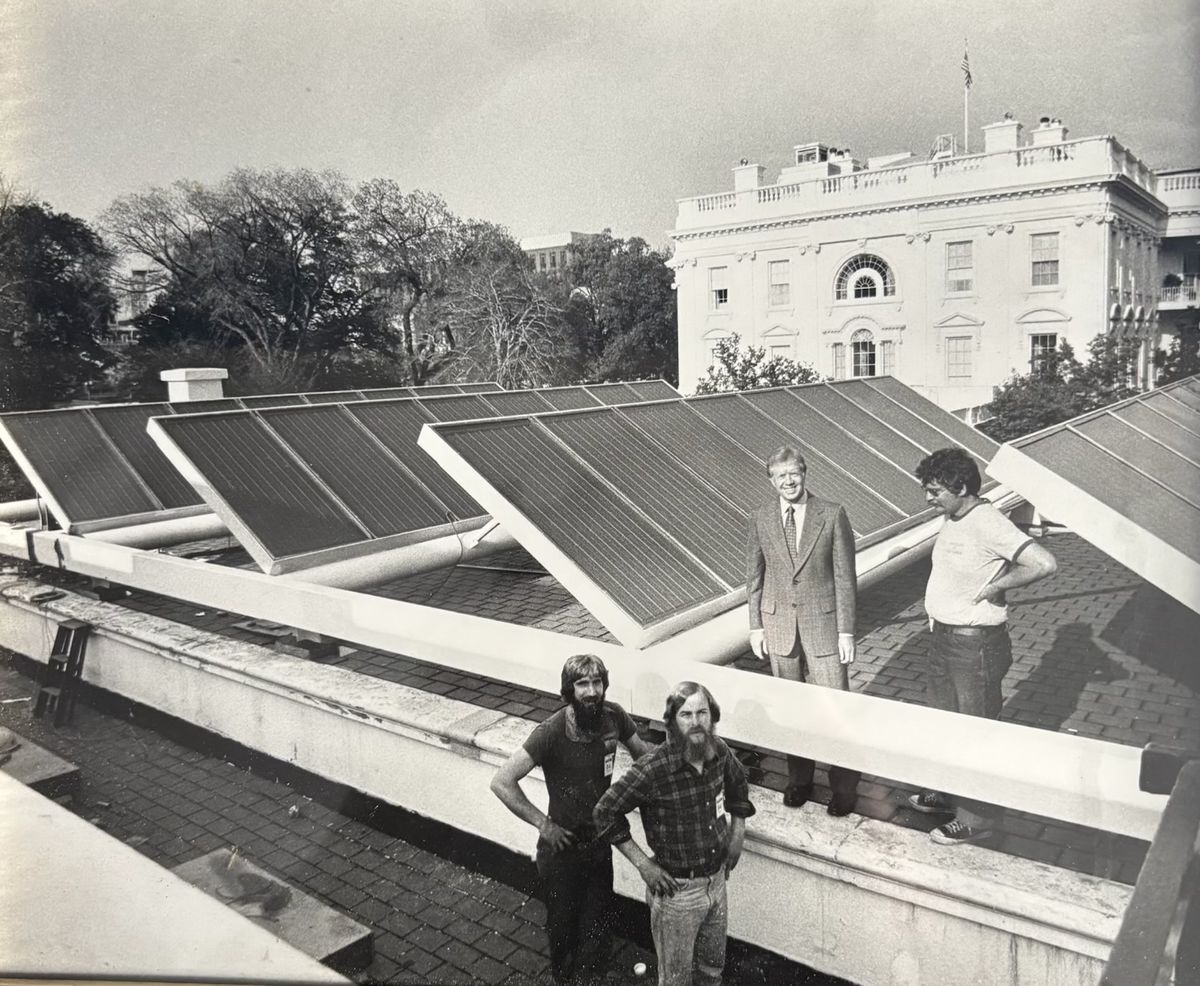

1979: President Jimmy Carter standing next to chief engineer Gordon Priess, Rick Schwolsky on the left foreground, and Ed Butler on the right, checking out the newly installed solar panels on the roof of the White House.
Photo provided by Ed Butler
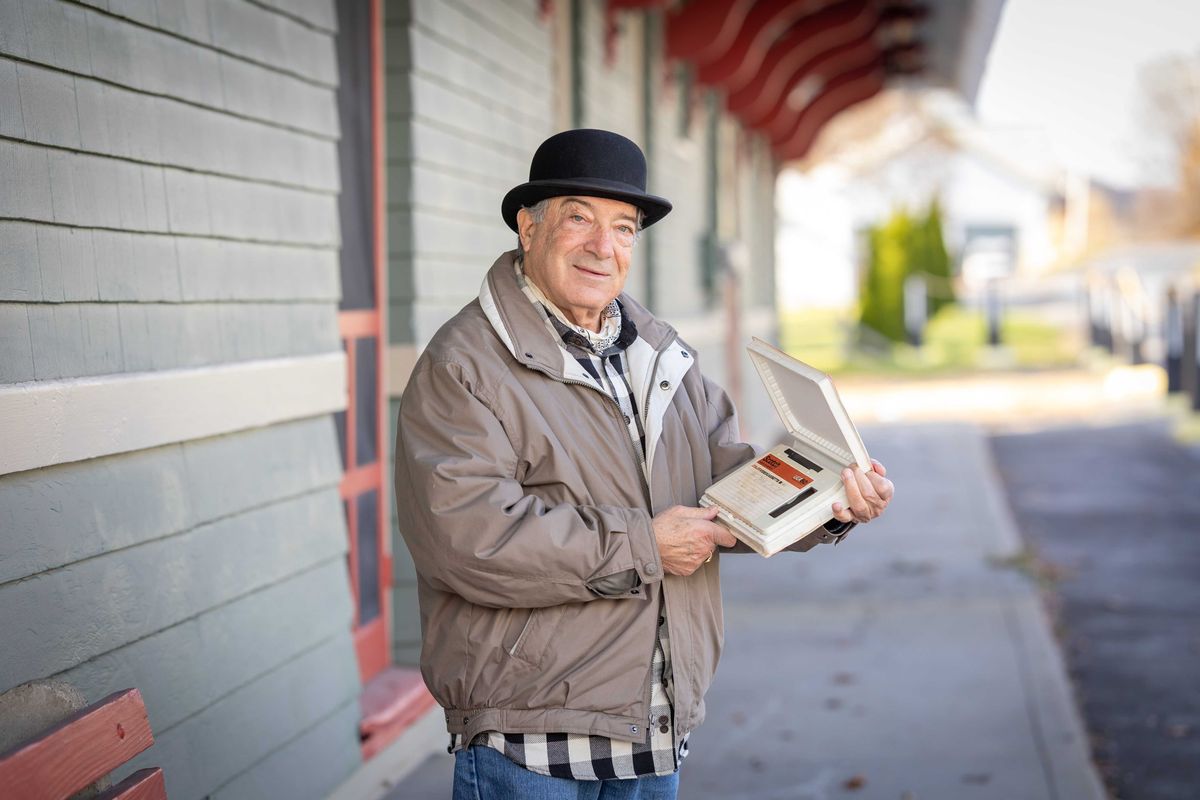
 Tom Strumolo of Norfolk, founder Energy General LLC, was on the crew that installed solar panels on the roof of the White House for President Jimmy Carter in 1979.Jennifer Almquist
Tom Strumolo of Norfolk, founder Energy General LLC, was on the crew that installed solar panels on the roof of the White House for President Jimmy Carter in 1979.Jennifer Almquist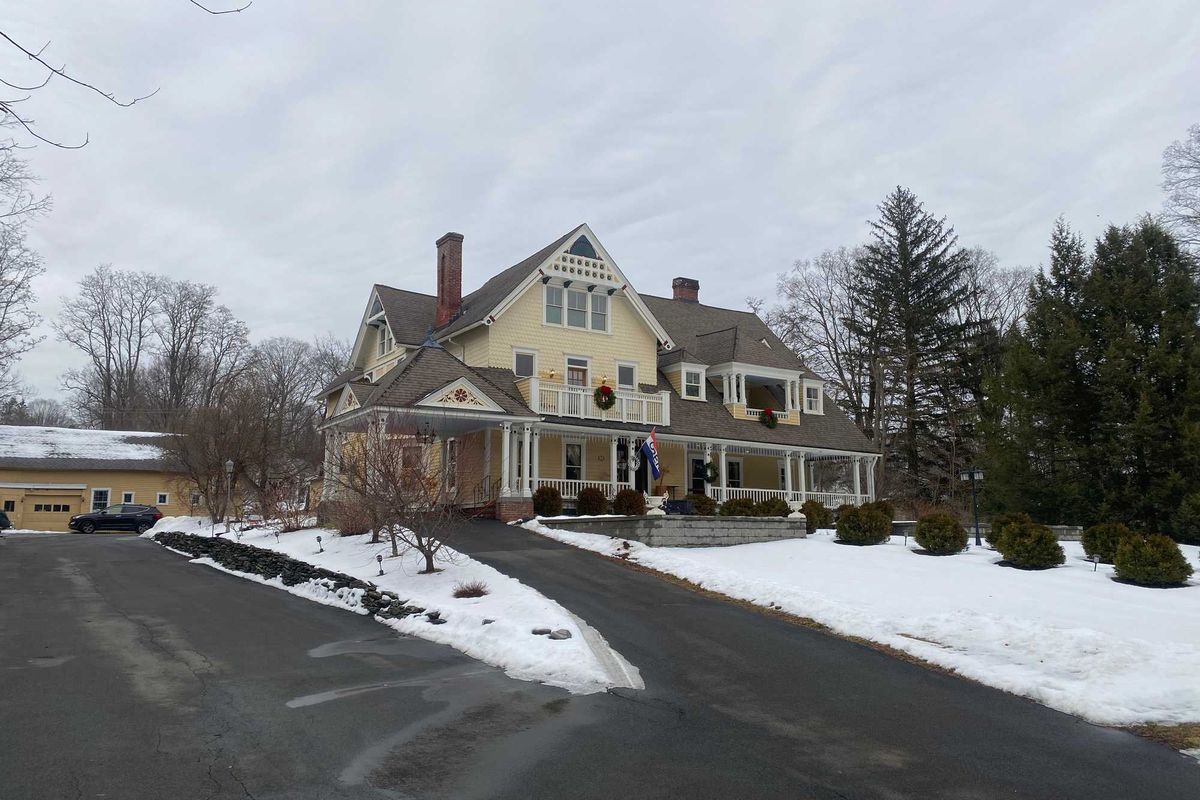
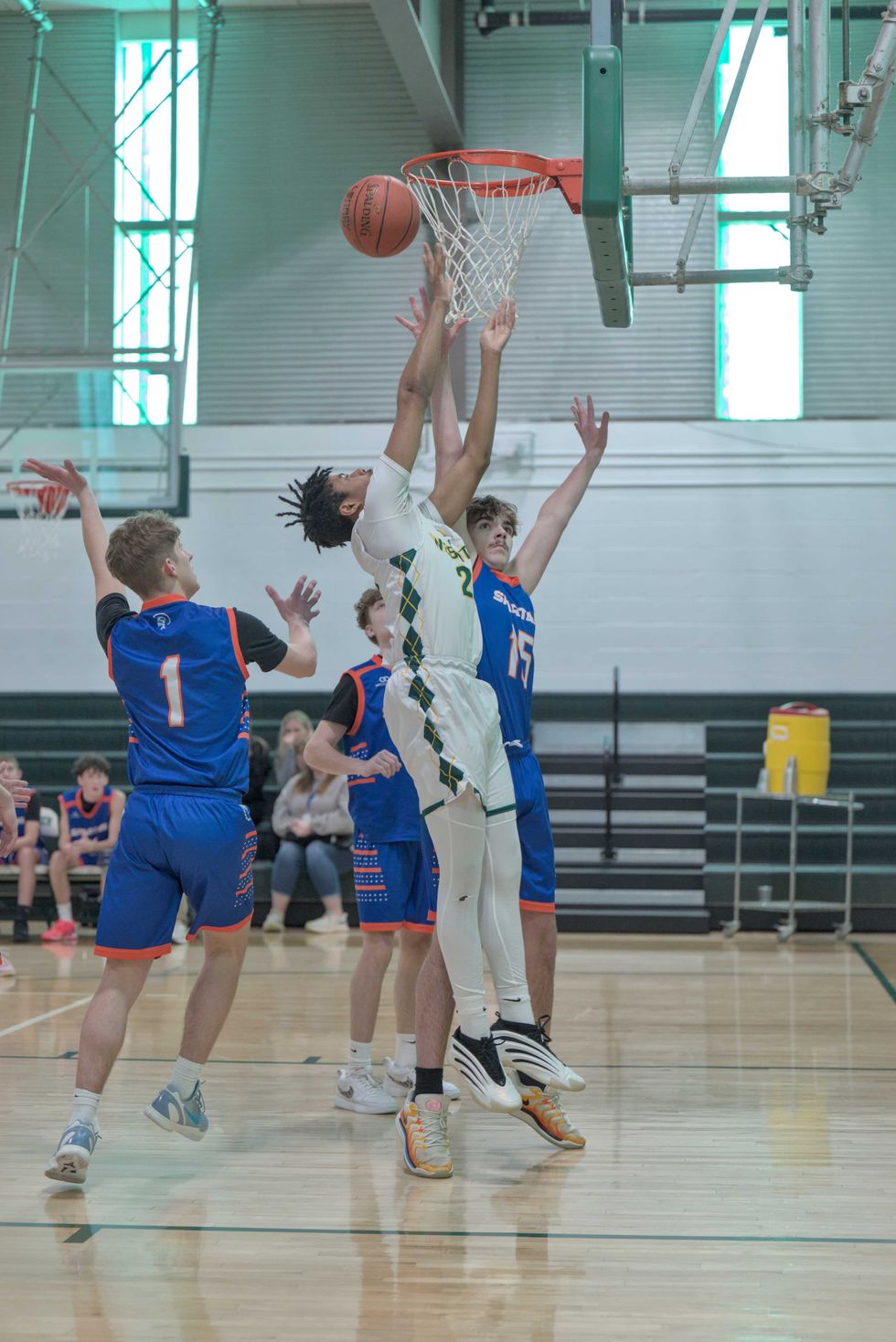
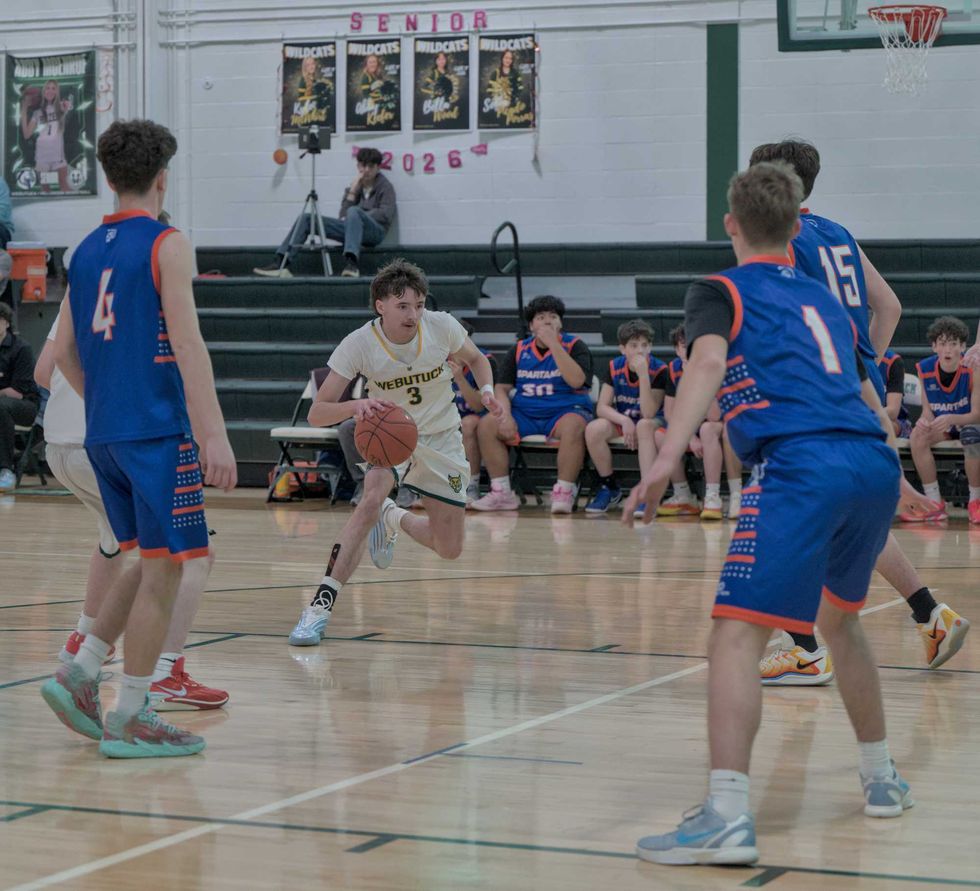
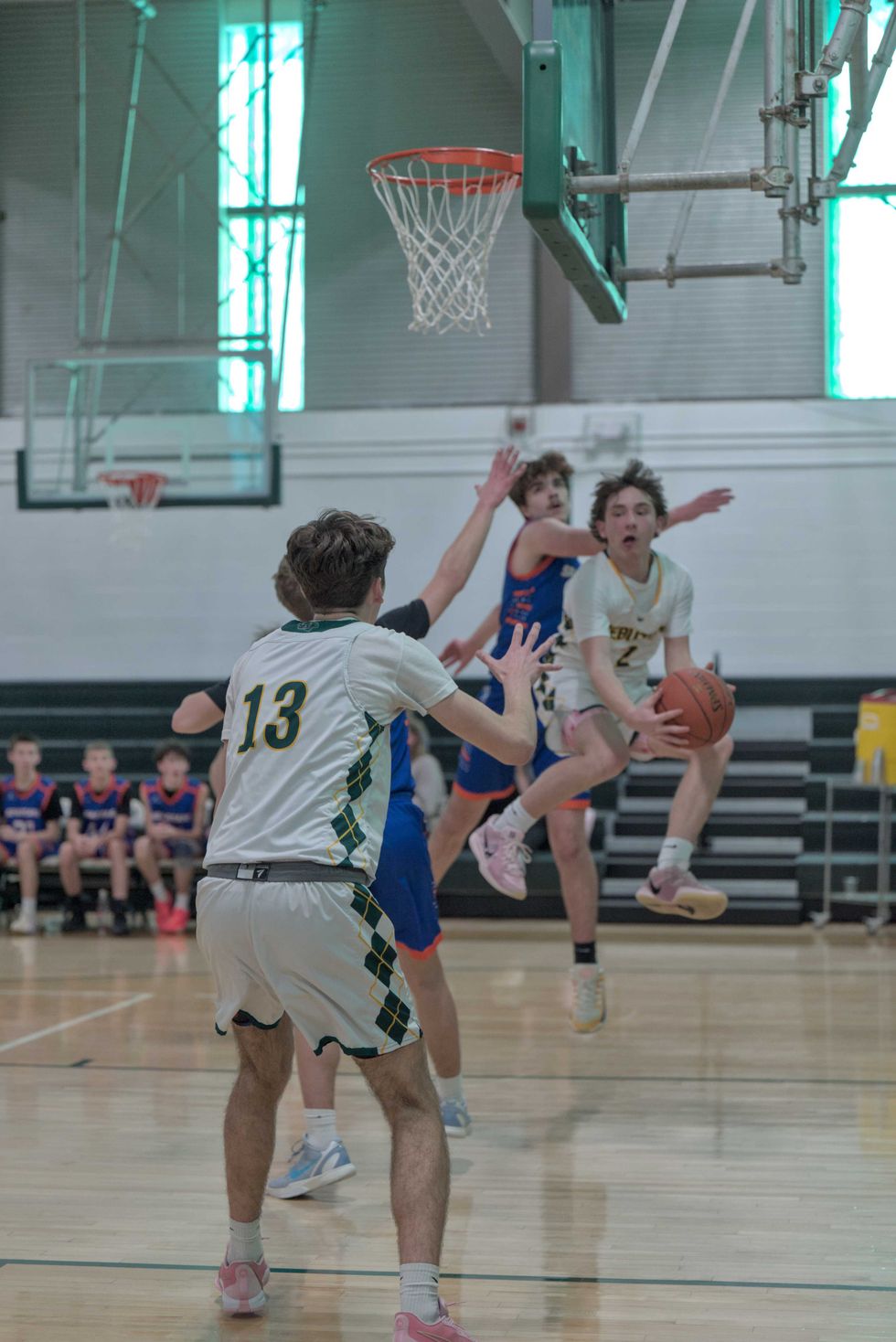
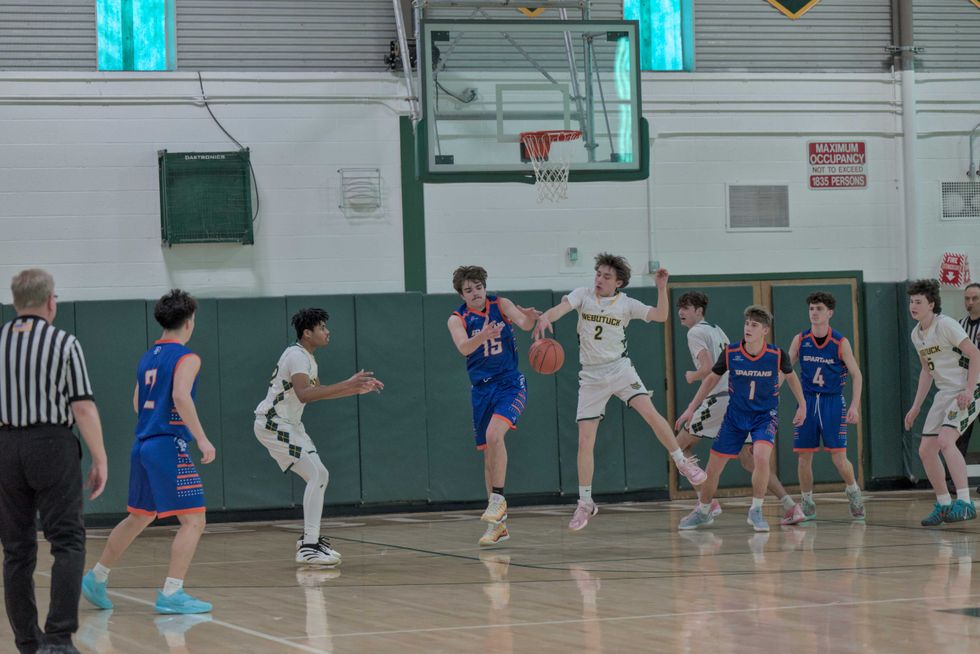
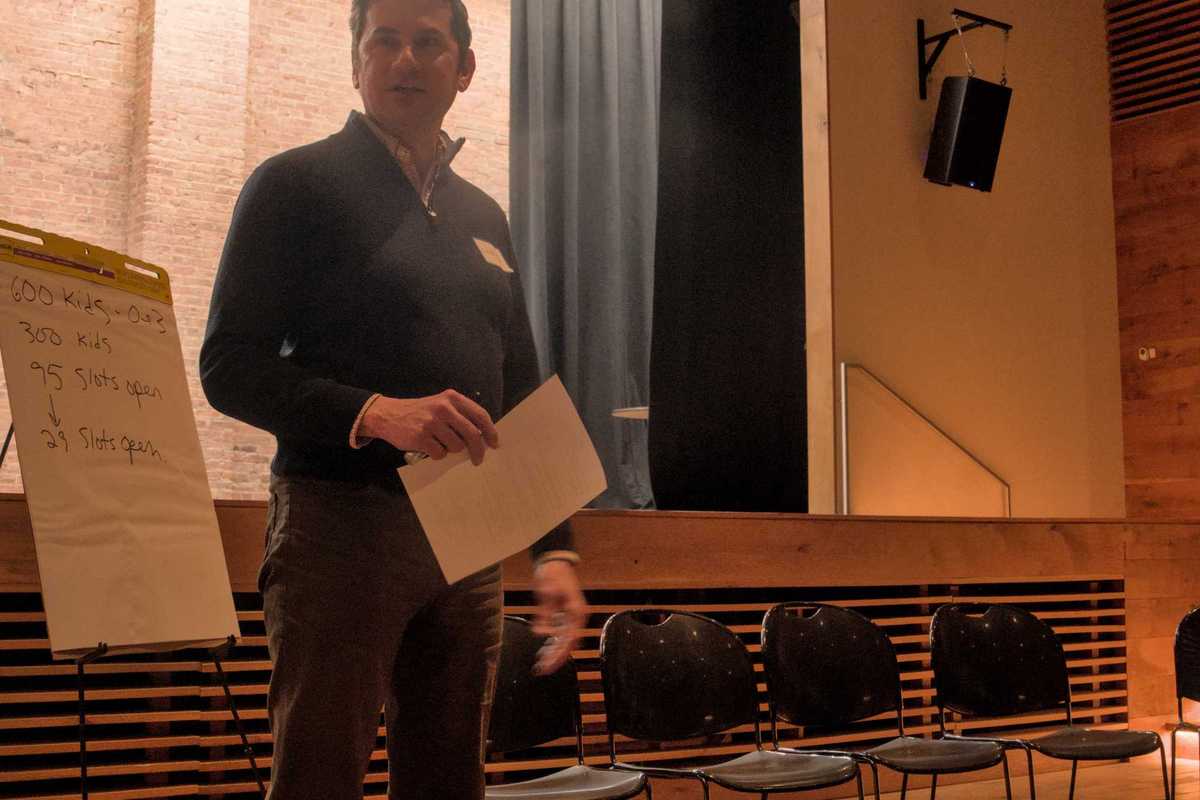
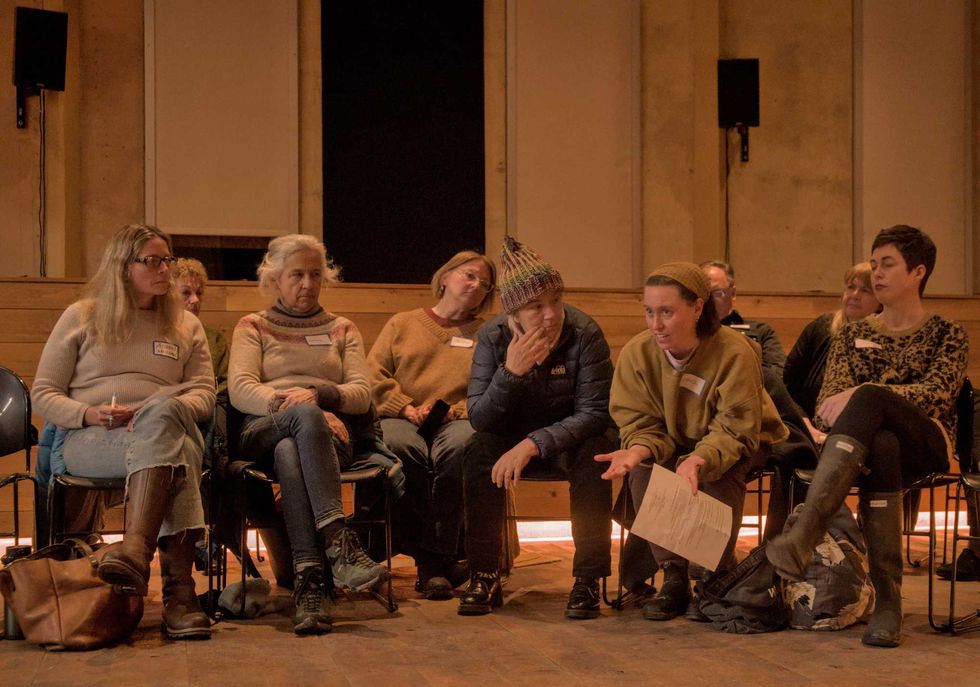


















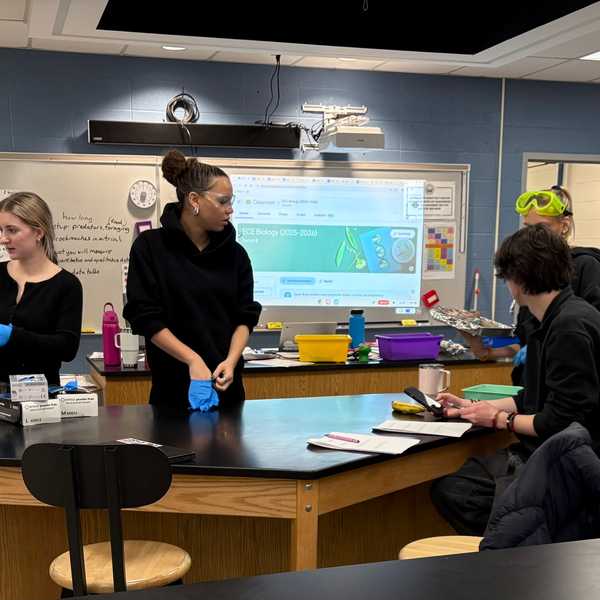
 Local parents, child care providers and nonprofit representatives outline the challenges they face in accessing and providing childcare in rural northeast Dutchess County during a forum at the Stissing Center in Pine Plains on Wednesday, Feb. 25. Photo by Nathan Miller
Local parents, child care providers and nonprofit representatives outline the challenges they face in accessing and providing childcare in rural northeast Dutchess County during a forum at the Stissing Center in Pine Plains on Wednesday, Feb. 25. Photo by Nathan Miller 

 lakevillejournal.com
lakevillejournal.com 
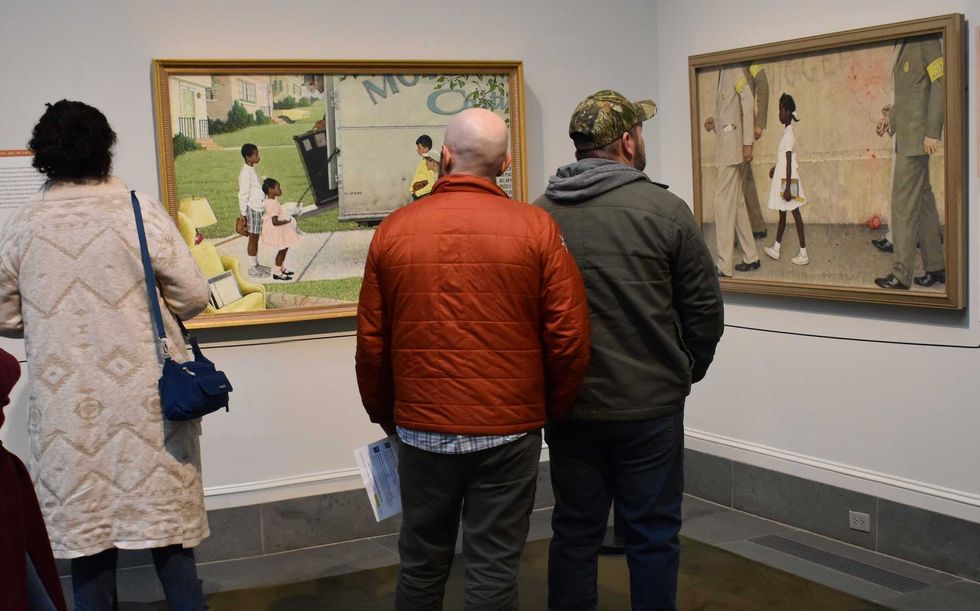



 Visitors consider Norman Rockwell’s paintings on Civil Rights for Look Magazine, “New Kids in the Neighborhood” (1967) and “The Problem We All Live With” (1963.) L. Tomaino
Visitors consider Norman Rockwell’s paintings on Civil Rights for Look Magazine, “New Kids in the Neighborhood” (1967) and “The Problem We All Live With” (1963.) L. Tomaino




