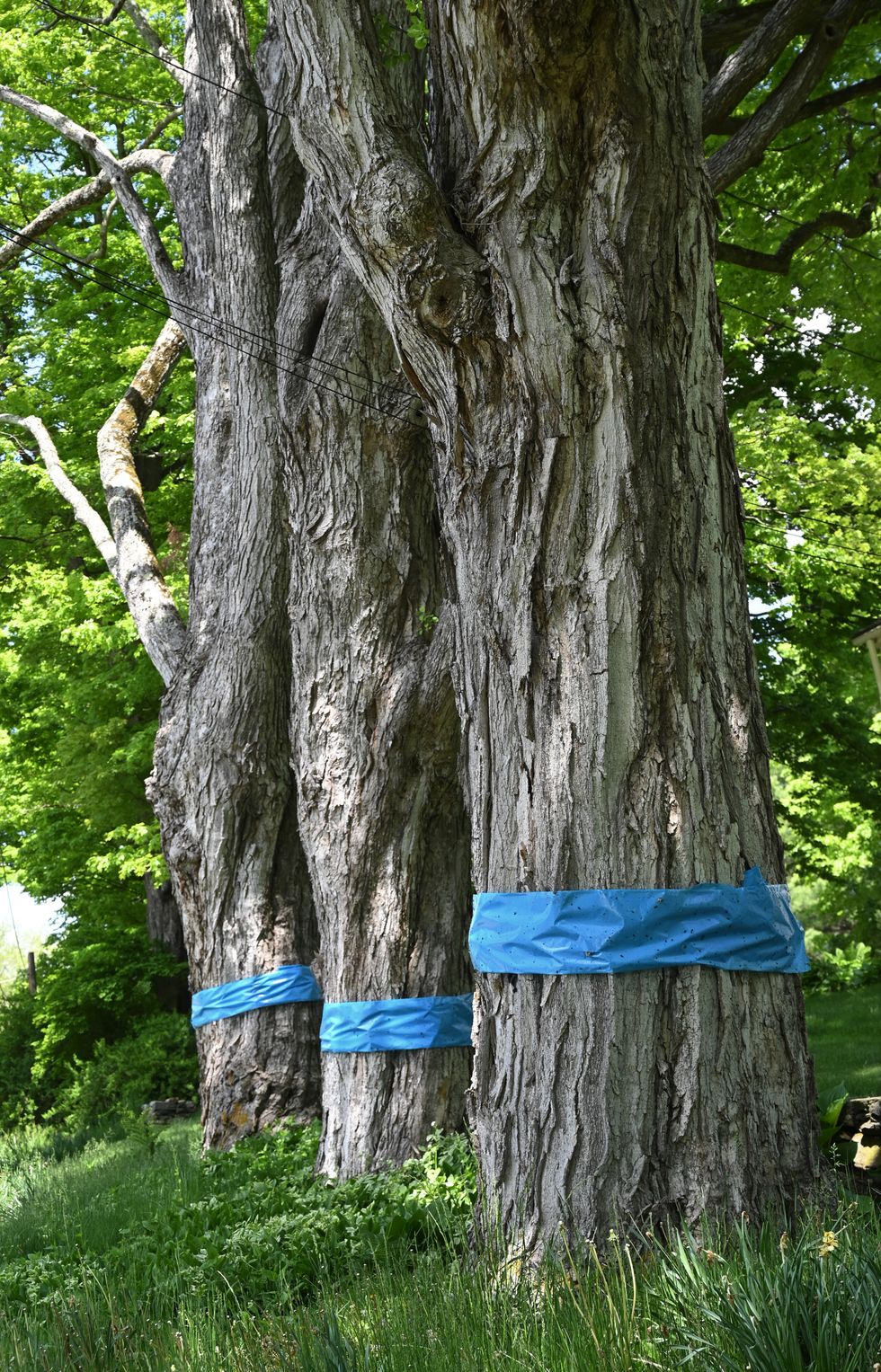
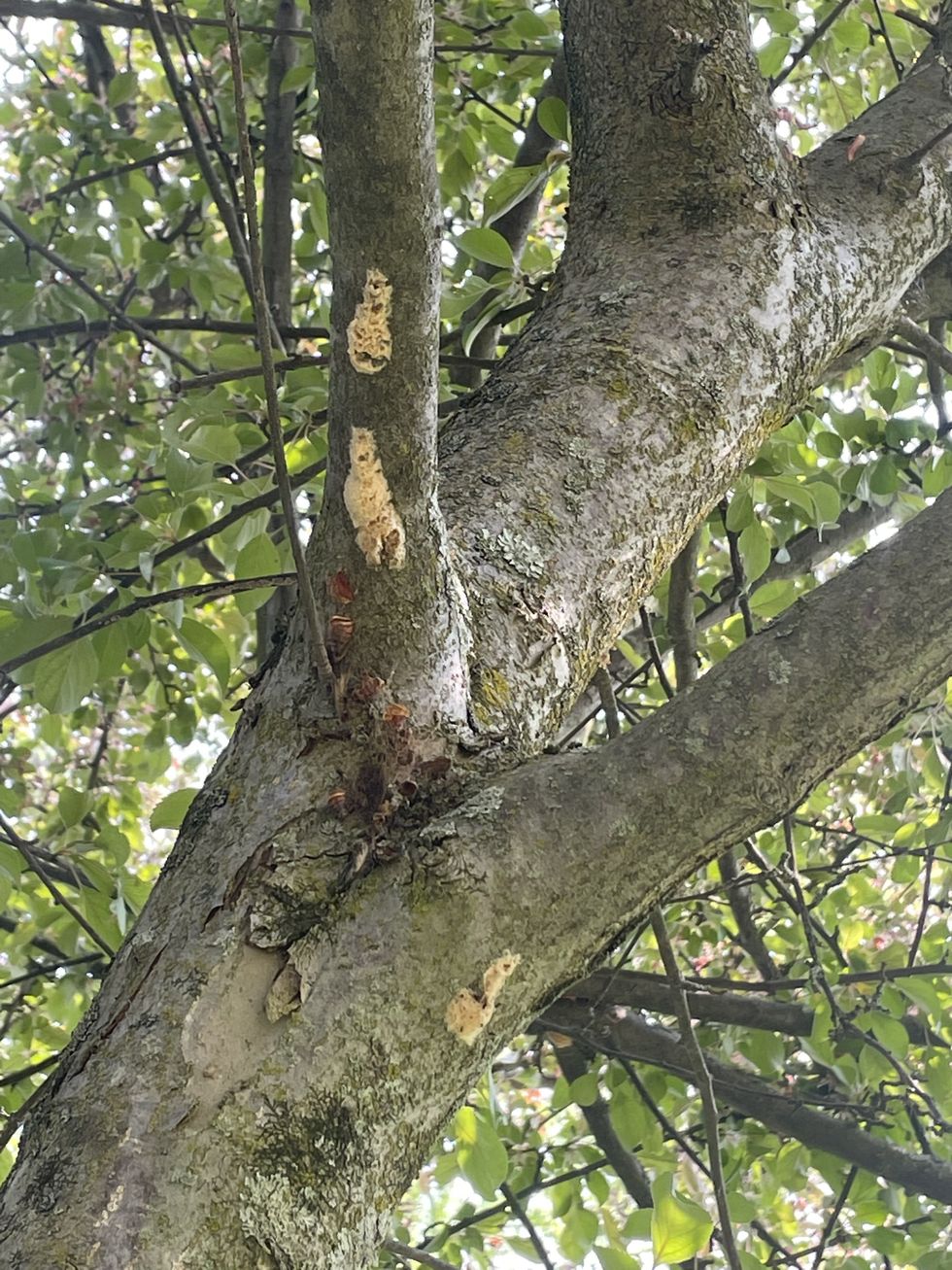
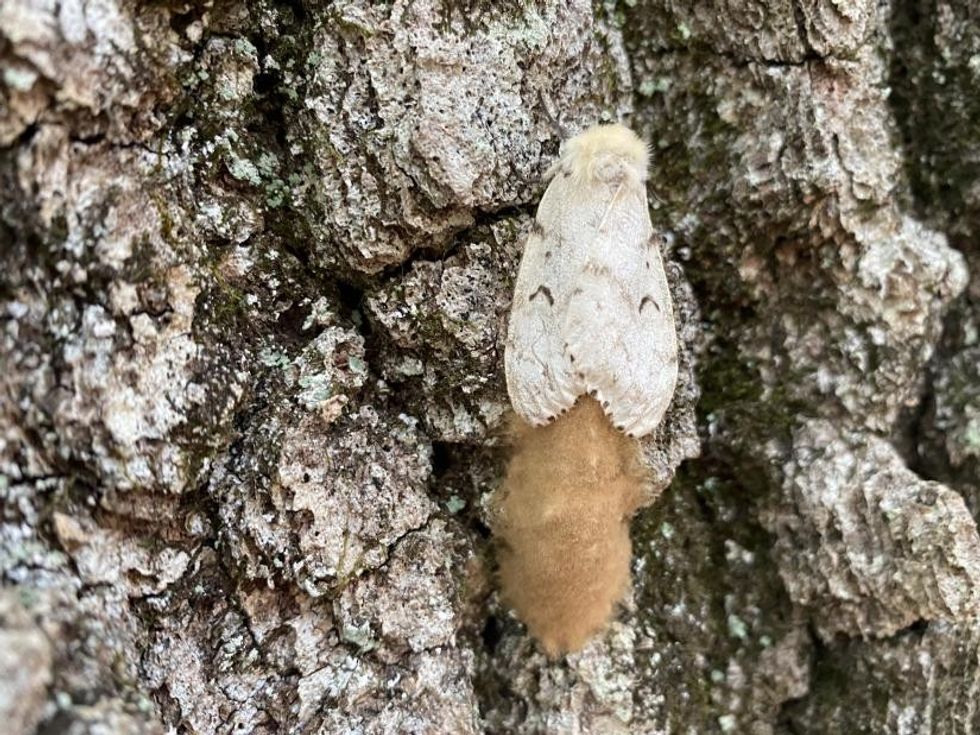
Latest News
In remembrance:
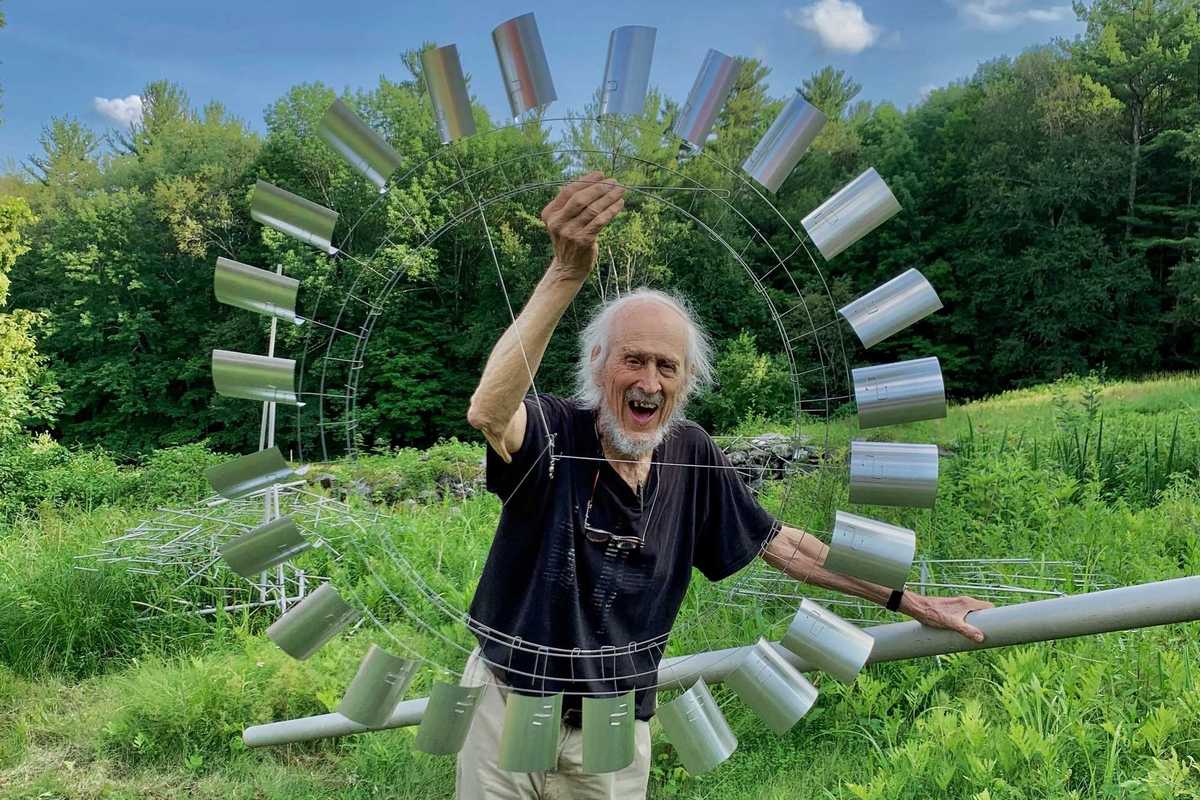
Tim Prentice and the art of making the wind visible
In remembrance:
Tim Prentice and the art of making the wind visible
There are artists who make objects, and then there are artists who alter the way we move through the world. Tim Prentice belonged to the latter. The kinetic sculptor, architect and longtime Cornwall resident died in November 2025 at age 95, leaving a legacy of what he called “toys for the wind,” work that did not simply occupy space but activated it, inviting viewers to slow down, look longer and feel more deeply the invisible forces that shape daily life.
Prentice received a master’s degree from the Yale School of Art and Architecture in 1960, where he studied with German-born American artist and educator Josef Albers, taking his course once as an undergraduate and again in graduate school.In “The Air Made Visible,” a 2024 short film by the Vision & Art Project produced by the American Macular Degeneration Fund, a nonprofit organization that documents artists working with vision loss, Prentice spoke of his admiration for Albers’ discipline and his ability to strip away everything but color. He recalled thinking, “If I could do that same thing with motion, I’d have a chance of finding a new form.”
What Prentice found through decades of exploration and play was a kind of formlessness in which what remains is not absence, but motion. To stand before one of his sculptures is to witness a quiet choreography where metal breathes, shadows shift and time softens.
After Yale, Prentice co-founded the architectural firm Prentice & Chan in 1965. The firm designed affordable housing projects in New York City, work largely led by partner Lo-Yi Chan. Prentice also designed custom single-family homes and continued to develop sculptural ideas alongside his architectural practice. After leaving the firm in 1975 and eventually relocating full time to Cornwall, he undertook a range of local architectural projects while increasingly devoting himself to sculpture.
Prentice began producing larger-scale sculptural commissions in the 1970s, during a period of national expansion in public art funding tied to new building projects. His first major commission came in 1976 from AT&T, helping launch a career that would bring his kinetic installations to corporate, institutional and public spaces across the United States and abroad. While his work follows in the lineage of Alexander Calder and George Rickey, critic Grace Glueck observed that its “gently assertive character is very much his own.”
In Cornwall, Prentice established a studio devoted to designing and fabricating kinetic sculpture, where he continued working for decades. He had many assistants over the years including local artists David Bean, Ellen Moon and Richard Griggs. David Colbert worked with Prentice for many years, assisting with fabrication, installation and project development and in 2012, Prentice established Prentice Colbert Inc., helping ensure that fabrication and development of large-scale commissions could continue beyond his lifetime.
Colbert said Prentice could be imperious, but came to understand that he valued thoughtful critique over agreement. “That evolved into a free and easy give-and-take, along with some fierce arguments,” he said. “Our relationship was always developing, right through to the end.”
In the mid-1990s, Prentice was diagnosed with macular degeneration, a condition that gradually narrowed his field of vision. Rather than turning away from the visual world, he leaned further into it, focusing on movement, light and peripheral perception — on what could be felt as much as seen. The Vision & Art Project film documents this period of his life and the ways he adapted his creative process.
Even in his final years, Prentice continued experimenting. In the summer of 2025, he created a series of drawings titled “Memory Trees,” produced from recollection as his eyesight declined. The series sold out at the Rose Algrant show that August, offering a poignant example of an artist adapting and creating throughout their lifetime.
“He was interested in whimsy,” said Nora Prentice of her dad. “But he also worked seven days a week,” she said. “He’d come in for dinner and then go right back out.” His studio was known for its atmosphere of curiosity and play, with music often drifting through the workspace as sculptures moved overhead in careful, measured rhythms. His work reminds viewers how profoundly small movements shape perception, and how change itself may be the only constant.
In his poem “Among School Children,” William Butler Yeats asks, “How can we know the dancer from the dance?” Prentice offered his own answer. “I’m not making the dance,” he said. “The wind is making the dance.”
As Nora reflected, “I think that’s how he would want to be remembered: for making the wind visible.”
Keep ReadingShow less
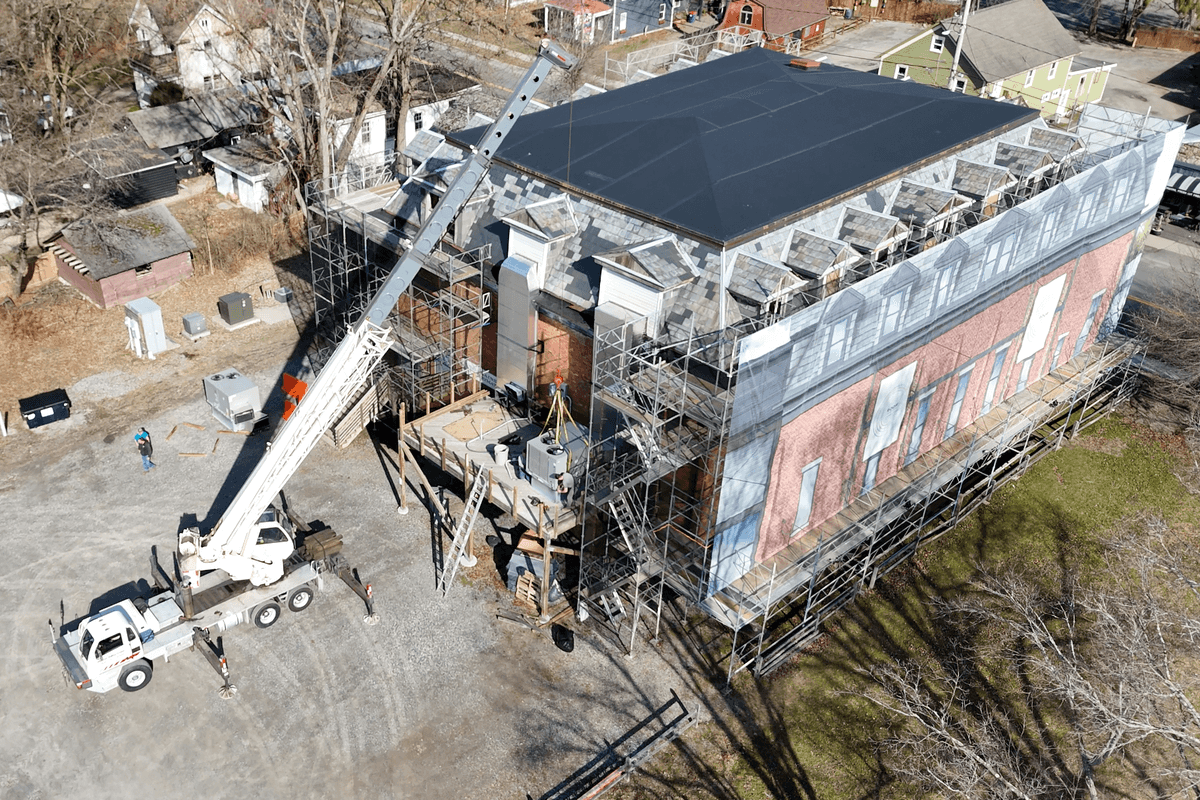
Hyalite Builders is leading the structural rehabilitation of The Stissing Center in Pine Plains.
Provided
For homeowners overwhelmed by juggling designers, architects and contractors, a new Salisbury-based collaboration is offering a one-team approach from concept to construction. Casa Marcelo Interior Design Studio, based in Salisbury, has joined forces with Charles Matz Architect, led by Charles Matz, AIA RIBA, and Hyalite Builders, led by Matt Soleau. The alliance introduces an integrated design-build model that aims to streamline the sometimes-fragmented process of home renovation and new construction.
“The whole thing is based on integrated services,” said Marcelo, founder of Casa Marcelo. “Normally when clients come to us, they are coming to us for design. But there’s also some architecture and construction that needs to happen eventually. So, I thought, why don’t we just partner with people that we know we can work well with together?”
Traditionally, homeowners hire designers, architects and contractors separately, a process that can lead to miscommunication, budget overruns and design revisions once construction begins. The new partnership seeks to address those challenges by creating a unified team that collaborates from the earliest planning stages through project completion.
“We can explore possibilities,” Marcelo said. “Let’s say the client is not sure which direction they want to go. They can nip that in the bud early on — instead of having three separate meetings with three separate people, you’re having one collaborative meeting.”
The partnership also reflects an expanded view of design, moving beyond surface aesthetics to include structural, environmental and performance considerations. Marcelo said her earlier work in New York City shaped that perspective.
“I had a 10-year career in New York City designing townhouses and penthouses, thinking about everything holistically,” she said. “When I got here and started my own business, I felt like I was being pigeonholed into only the decorative part of design. With the weight of an architect on our team now, it has really helped us close those deals with full home renovations, ground up builds and additions.”
The team emphasizes what it describes as high-performance design, incorporating modern building science, energy efficiency and improved air quality alongside aesthetic goals.
“If you’re still living inside 40-year-old technology and building techniques, we haven’t really handed off the best product we could,” said Soleau. “The goal is to not only to reach that level of aesthetic design but to improve the envelope, improve the living environment within a home and bring homes up to elevated standards of high-performance building.”
This integrated approach has proven particularly useful for renovation projects, where modern materials and systems can be thoughtfully incorporated into older structures. The firms also prioritize durability and long-term functionality, often incorporating antiques, vintage elements and high-quality materials designed to support clients’ lifestyles.
“I’m very big on investing in pieces that are going to be quality and last you the test of time,” Marcelo said. “Not just designing for a five- to 10-year run, but really designing for the long haul.”
The collaboration is already underway on several projects, including a major renovation in Sharon that involves rebuilding a 1990s modular home to maximize views while upgrading structural and performance systems. The firms are also exploring advanced visualization technology that would allow clients to experience projects through virtual reality before construction begins.
“For me, as somebody who wants to take the project all the way from beginning to end and make the process as effortless as possible for my client, it’s easier to do that with collaboration and a team than to do it alone,” Soleau said. “Most clients, especially second-home owners, want a team that can lead the project from concept through completion; aligning design, budget, and construction.”
On Feb. 19, the three firms will officially launch the initiative at an invitation-only event at The Stissing Center in Pine Plains, where Hyalite Builders is leading the structural rehabilitation of the historic building. A limited number of “hard hat tour” reservations will be available by request, providing rare, behind-the-scenes access while work is actively underway. Those interested in attending may contact event organizer Lauren Fritscher of Berkshire Muse at hello@berkshiremuse.com.
Keep ReadingShow less
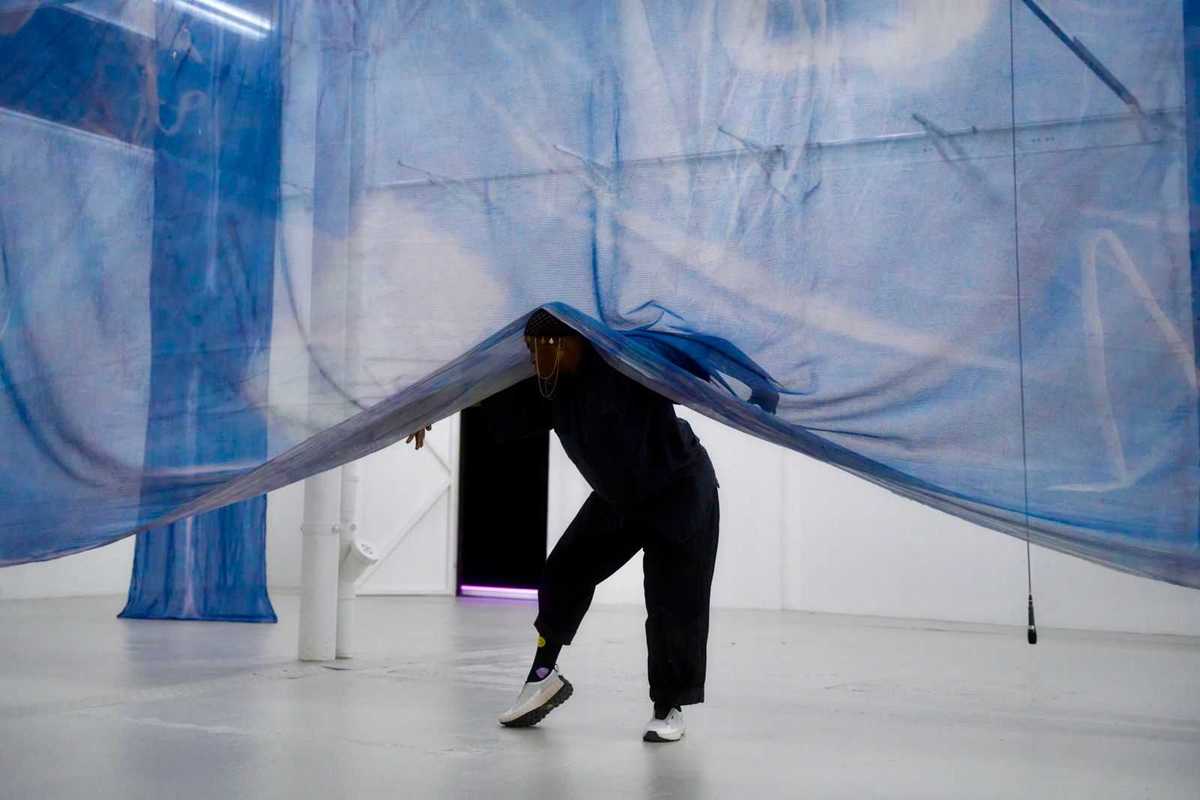
Autumn Knight will perform as part of PS21’s “The Dark.”
Provided
This February, PS21: Center for Contemporary Performance in Chatham, New York, will transform the depths of midwinter into a radiant week of cutting-edge art, music, dance, theater and performance with its inaugural winter festival, The Dark. Running Feb. 16–22, the ambitious festival features more than 60 international artists and over 80 performances, making it one of the most expansive cultural events in the region.
Curated to explore winter as a season of extremes — community and solitude, fire and ice, darkness and light — The Dark will take place not only at PS21’s sprawling campus in Chatham, but in theaters, restaurants, libraries, saunas and outdoor spaces across Columbia County. Attendees can warm up between performances with complimentary sauna sessions, glide across a seasonal ice-skating rink or gather around nightly bonfires, making the festival as much a social winter experience as an artistic one.
The Dark’s lineup includes several world and U.S. premieres. Highlights include Thomas Feng performing “Night Prayers,” a program of compositions by late Ethiopian composer and Orthodox nun Emahoy Tsegué-Maryam Guèbrou; Phil Kline’s outdoor participatory score “Force of Nature (February);” an audiovisual collaboration between composer David Lang and Academy Award-nominated filmmaker Bill Morrison; an interdisciplinary performance by Lee Ranaldo of Sonic Youth and multimedia artist Leah Singer; and “We Survived the Night: A Coyote Story in Four Parts” by Julian Brave NoiseCat.
For more information about The Dark or to purchase tickets, visit ps21chatham.org/the-dark
Keep ReadingShow less
loading